Relations between Africa and China are strengthening year in year out, with Chinese investment significantly impacting every sector, from mining, telecommunications to logistics and transportation. The Incept states, “Trade between China and Africa has risen from $765 million to more than $170 billion in the last 40 years.” It’s a logical move for China considering its population of approximately 1.4 billion and an economy starting to boom. China views these undeveloped nations as an opportunity to strengthen its economy further, with the continent now coming online, China’s positioning is a force to be reckoned with.
Mining

The land of the Sahara is resource-rich and ripe for growth, with China keen to collaborate, especially in the mining sector.
According to Investopedia, “Africa is estimated to contain 90% of the entire world supply of platinum and cobalt, half of the world’s gold supply, two-thirds of world manganese and 35% of the world’s uranium.”
China imports billions of dollars worth of base metals every year, consuming over twenty-five percent of the world’s supplies, it’s becoming heavily reliant on materials such as cobalt and manganese. The import of these materials will continue to boost its economy. With China said to be importing approximately $100 billion each year in base metals alone, African mining is a critical aspect of the East’s future prosperity.
Silk road
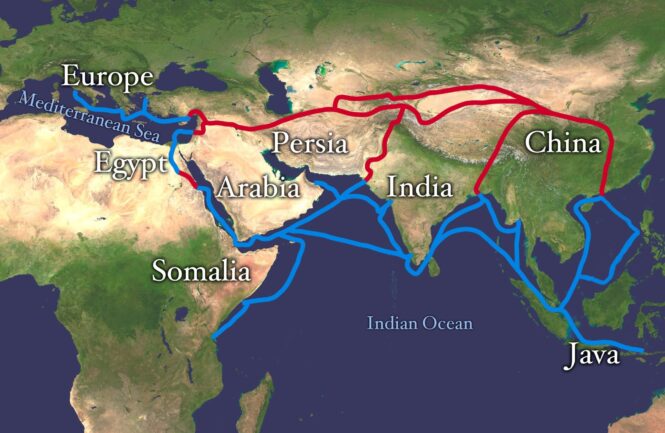
The ancient Silk Road is being revived, connecting to Africa, prompting greater trade between the nations. The Silk Road isn’t defined by a new set of ‘roads’, but instead by a complex transport system and network including roads, ports, pipelines, energy, and railways.
According to logistics software company CartonCloud, African transport, and logistics opportunities are on the rise, as the redevelopment and expansion of the Silk Road continue, huge advancements are being made, allowing for greater business opportunities.
The tragedy is that much of the work needed to put the infrastructure in place has been given to Chinese workers instead of locals, supporting the Chinese workforce, not the African. Hopefully, in the future, laws will be put in place to guarantee more work for local people, but that is yet to be seen.
Technology

DW states, “Made in China” technology now serves as the backbone of network infrastructure in several African countries, unbeknownst to millions of users.” China has a stronghold in telecommunications across the nations, ensuring that the majority of all phones and internet services are run by Chinese corporations and government regulators. To the rest of the world Huawei, the telecommunications giant, is a serious threat, with evidence suggesting spying on people through the use of its technology.
Security and surveillance issues aside, by and large Africa has ignored the threats posed by the Chinese government and seems content continuing to allow Chinese technology to support its people. There is also an upside, as technology allows for greater advancement in a whole host of areas including sanitation and safety.
“Most of the smart city projects that involve Chinese financing and companies in African countries are aimed at making cities safer — with surveillance systems. No one knows whether they could be used to crack down on government dissent.” DW states.
From technology, transport to mining, China’s influence and power across the continent is substantial. For better or worse, it’s clear that the future of Africa is in China’s hands.
 Imagup General Magazine 2024
Imagup General Magazine 2024



