When it comes to maintaining vehicle performance and reliability, few components are as vital as the cooling system. The cooling system is responsible for preventing the engine from overheating and ensuring that all components operate within safe temperature limits.
Without effective cooling, an engine can quickly suffer severe damage, leading to costly repairs and reduced efficiency. Understanding how these systems work, the types available, and the role of engine coolers can help car owners and mechanics make informed maintenance and upgrade decisions.
The Importance of Engine Cooling
Every combustion engine generates heat as a by-product of fuel ignition. While some heat is necessary for efficient combustion, excessive temperatures can warp engine parts, degrade lubricants, and lead to complete engine failure. The cooling system ensures that heat is absorbed, transferred, and dissipated away from critical components, allowing the engine to run smoothly and efficiently.
In modern vehicles, maintaining an optimal operating temperature is crucial not only for mechanical performance but also for emissions control and fuel economy. A well-functioning cooling system helps keep the engine running at its designed temperature, ensuring consistent performance and longevity.
How Engine Cooling Systems Work
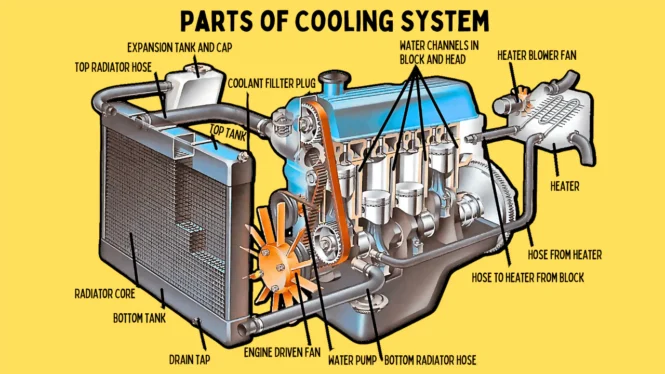
The process begins with a coolant fluid—typically a mix of water and antifreeze—that circulates through the engine block and cylinder head. As the coolant absorbs heat, it travels through a series of hoses to the radiator, where the heat is released into the surrounding air. A thermostat regulates the coolant flow, ensuring the engine warms up quickly when started and prevents overheating once it reaches operating temperature.
Other components, such as water pumps and fans, assist in maintaining steady coolant circulation and airflow. The water pump moves coolant through the system, while the fan draws air across the radiator to enhance cooling, especially when the vehicle is stationary or moving slowly.
Types of Cooling Systems
There are two main types of cooling systems used in vehicles: liquid cooling and air cooling.
- Liquid Cooling
This is the most common method used in modern cars. It relies on coolant circulating through the engine and radiator to remove heat. Liquid cooling offers more precise temperature control, making it ideal for high-performance and heavy-duty vehicles. - Air Cooling
This system is found primarily in older models and motorcycles. Instead of liquid coolant, it uses air to dissipate heat from metal fins attached to the engine. Air cooling is simpler and lighter but less efficient, particularly in large or high-powered engines.
Signs of Cooling System Problems
A malfunctioning cooling system can cause significant issues if not addressed promptly. Common warning signs include rising engine temperature, coolant leaks, strange noises from the water pump, or visible steam from under the bonnet. Drivers may also notice a sweet smell, which is often a sign of leaking coolant.
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to overheating, cracked cylinder heads, or even complete engine failure. Routine inspections, regular coolant changes, and prompt repairs are essential to prevent damage and maintain optimal performance.
Upgrading Cooling Systems for Performance
Performance vehicles and heavy-duty machinery often require enhanced cooling solutions to handle increased heat loads. Upgraded radiators, high-flow water pumps, and performance thermostats can significantly improve heat dissipation. For engines that operate under extreme conditions—such as racing or towing—additional cooling components like oil coolers or transmission coolers are often installed.
This is where engine coolers come into play.
The Role of Engine Coolers in Vehicle Performance
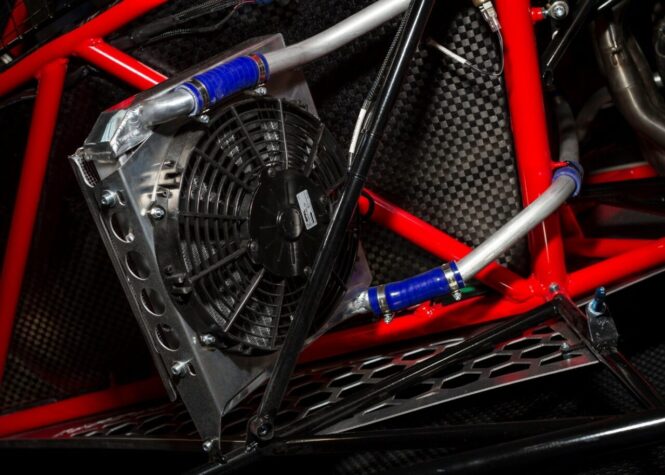

Engine coolers are designed to regulate temperatures in various parts of the engine, particularly where oil or transmission fluid can become excessively hot. These devices work by circulating fluids through a cooling element, transferring heat away before the fluids re-enter the engine or gearbox. The result is improved performance, extended component life, and reduced risk of overheating.
High-performance and off-road vehicles often use aftermarket engine coolers to handle increased stress and maintain consistent operation under demanding conditions. By keeping vital fluids at optimal temperatures, they help prevent breakdowns and maintain efficiency. Investing in high-quality coolers, such as those available from engine coolers, ensures better reliability and protection for any engine operating under heavy load or extreme heat.
Maintenance Tips for a Healthy Cooling System
To ensure the longevity of your cooling system, regular maintenance is essential. Check coolant levels frequently and top up with the manufacturer-recommended fluid. Inspect hoses, clamps, and connections for any signs of wear or leakage. It’s also wise to flush the system periodically to remove debris and old coolant that can reduce efficiency.
Monitoring engine temperature while driving is equally important. If the gauge begins to climb unexpectedly, it’s best to stop and investigate rather than risk serious damage. Early detection and preventative care can save both time and money in the long run.
Final Thoughts
A vehicle’s cooling system is often overlooked until problems arise, yet it plays one of the most critical roles in maintaining performance and preventing damage. Understanding its components and ensuring it’s properly maintained can make all the difference in engine lifespan and reliability. For those seeking enhanced performance or protection in extreme conditions, upgrading with quality engine coolers can offer a practical and effective solution.
The Future of Engine Cooling Technology

As automotive innovation accelerates, the future of engine cooling systems is shifting toward smart, adaptive, and sustainable designs. Electric and hybrid vehicles, for instance, require advanced thermal management not just for engines but also for batteries, inverters, and power electronics. Intelligent cooling modules with electronic pumps and variable-speed fans are increasingly replacing traditional mechanical systems, improving precision while reducing energy waste.
New materials such as lightweight aluminum alloys and nano-coated heat exchangers are enhancing heat transfer efficiency while minimising corrosion. Moreover, eco-friendly coolants and closed-loop thermal systems are helping manufacturers meet stringent environmental regulations.
In the years ahead, expect to see greater integration between cooling systems, vehicle sensors, and onboard computers, creating a dynamic feedback network that continuously adjusts performance in real time. This evolution will not only extend engine life and reduce emissions but also redefine efficiency standards across the entire automotive industry — ensuring that vehicles remain powerful, sustainable, and reliable for generations to come.
 Imagup General Magazine 2025
Imagup General Magazine 2025